“∞” is the symbol for what “number” in mathematics, used to represent when a value is too high to count?

What is the distance around a circle called?
How many sides does a decagon have?

Which of these numbers is largest?
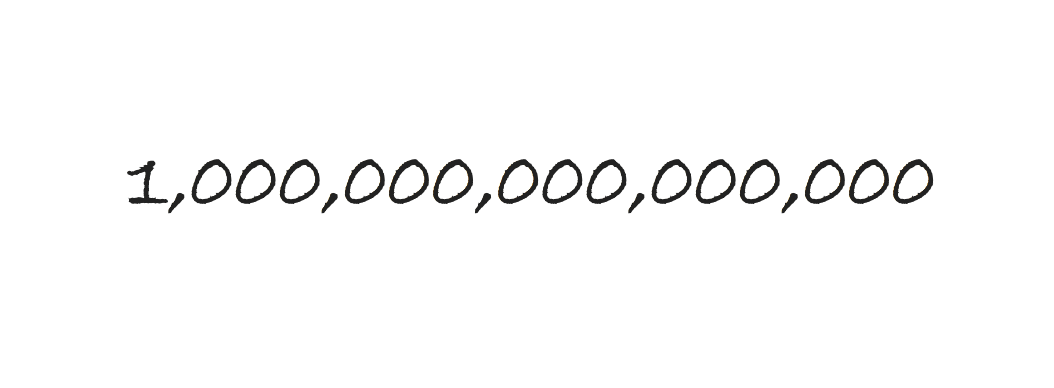
Which of these traffic sign is in the shape of an octagon?

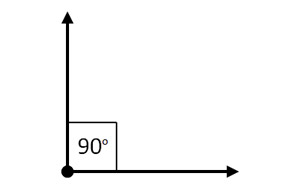
What is the special name given to an angle that is exactly 90 degrees?
Which of these prefixes mean “5”?
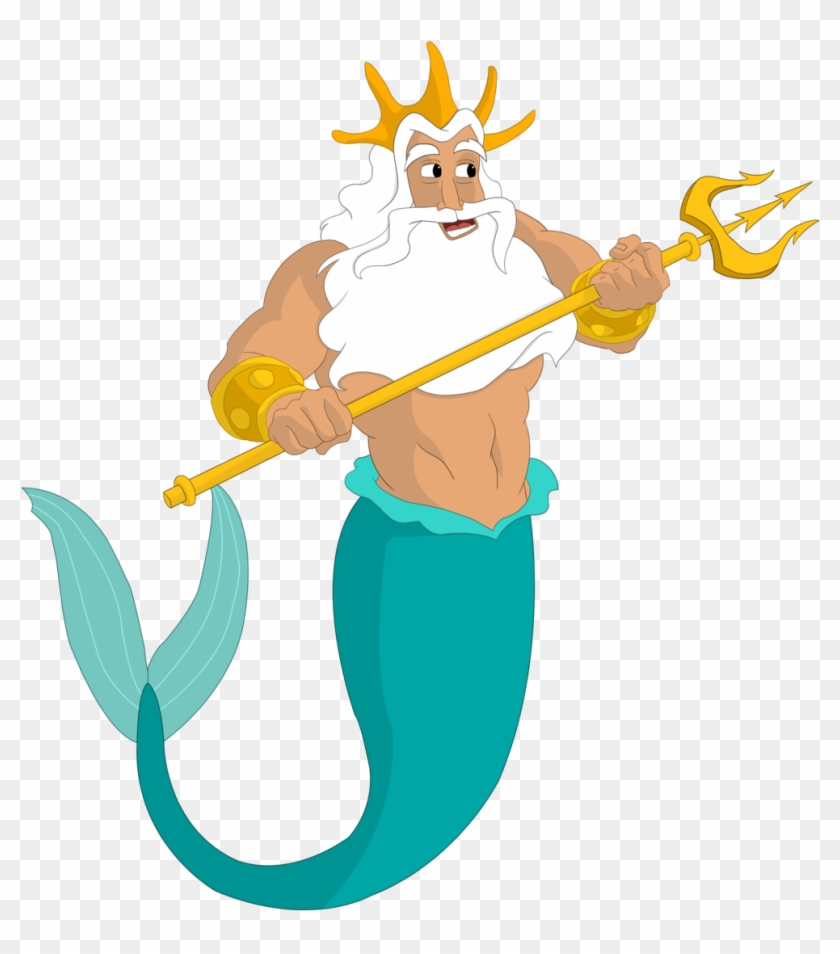
In “The Little Mermaid,” Ariel’s father (King Triton) carried a three-pronged spear. Use the number of prongs on the spear to correctly identify the name of the spear. What is the name of this spear?

What is the proper Order of Operations?

What is the name for a special sequence or series of numbers where every number after the first two is the sum of the two preceding ones?

What is the name for the longest side of a triangle?
The distance around a rectangle is called what?
A table has 10 columns and 10 rows. To find out how many cells are in the table, what operation do you use?

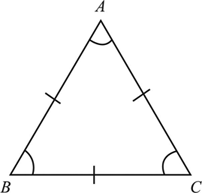
What kind of triangle has all three sides the same length?
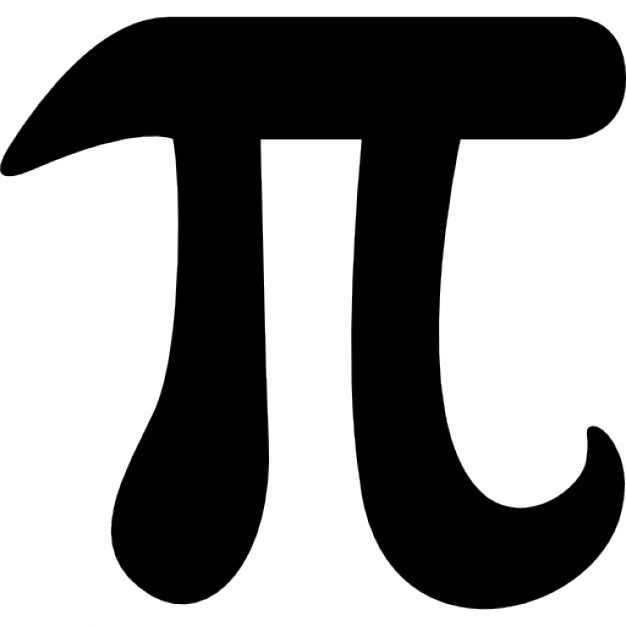
There is a special number in mathematics that is equal to approximately 3.14. What is its name?